What is the P0429 fault code What is the Catalyst Heater Control Circuit Bank 1 malfunction description? How can you fix the P0429 fault? What are the symptoms and causes of the P0429 error code?
What is the P0429 Fault code? What does it signify?
The malfunctioning of heated oxygen sensors is the reason for the P0429 code. It means that one or more of the heated oxygen sensors has failed. The engine bank that contains cylinder 1 is called “Bank 1”. An electrical fault in the circuit, or an incorrectly reading sensor can cause this code to be hidden.
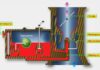
The heated catalytic convert’s primary function is to reduce the exhaust emissions of vehicles that use gasoline or diesel engines. It is a dense filter element that contains ceramic fibers and precious metals. The steel casing protects it from the exhaust pipe. After passing through the heated catalyst, harmful oxides of nitrogen (N2O), and carbon monoxide are converted to harmless ions of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water. These processes can be performed with the engine exhaust heat and the filtering element.
Modern diesel-powered vehicles have the SCR system, which helps to lower their emissions. The powertrain control module (PCM) injects an exhaust fluid (DEF/Adblue) at specific times into the exhaust pipe to increase the efficiency of the catalyst. A standard catalytic converter should reach temperatures of up to 800°F (426°C). For heated catalytic converters, this value should be at least 1,200°Fahrenheit (648°C).
Up and down oxygen (O2) sensors, as well as exhaust temperature sensors, are used to monitor the catalytic converter’s efficiency. The exhaust system has one sensor before the catalyst, and one after it.
O2 sensors control the amount of oxygen in exhaust gases and send it to the exhaust system. These sensors produce a voltage signal according to the amount of oxygen in exhaust gases and give information to the PCM. The heated catalyst will not function properly if it isn’t working correctly. This condition will be detected by the PCM and it will set a P0429 Code.
The P0429 fault code can be applied to vehicles of all makes and models, including but not limited to Toyota, Mercedes Benz. Subaru, Suzuki. Audi, Honda. Nissan. GM.
What causes the P0429 Fault code?
Below are some reasons to set fault code P0429:
- – The Catalyst temperature sensors harness can be either cut or completely open
- – The catalyst temperature sensor circuit has a loose or poor connection
- – Defective catalyst temperature sensor
- – Wrong or missing diesel exhaust fluid (DEF / Adblue)
- – Diesel exhaust fluid injection system failure
- – Defective O2 sensors
- – Defective catalytic convertor
- – Engine exhaust leaks
What are the symptoms of P0429 Fault code?
These symptoms may be present in vehicles with code P0429.
- – Illumination at the check engine lights
- – The PCM may activate the failsafe mode when it senses that the O2 sensor circuit heater circuit is low.
- – Low engine performance
- – Increased fuel consumption
- – A rise in exhaust emission values
- – Exhaust fumes emitting black smoke
- – Setting related fault codes
How to Fix the P0429 Fault Code
There are several repairs that can resolve the P0429 fault code.
- – Repair of damaged wires and loose connections to the catalyst temperature sensor
- – Repairing short circuit or open temperature sensor problems
- – Replacing faulty temperature sensor catalyst
- – Check the diesel exhaust fluid and top it up if necessary
- – Repair the diesel exhaust fluid injection (blown relays and fuses should be replaced).
- – Replacing the damaged catalytic convert
- – Repair engine exhaust leaks