What is ABS Sensor? What are the symptoms for ABS sensor malfunction? What does the ABS sensor do? …..Active and passive ABS sensors
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), a sophisticated braking system, is used extensively in modern cars. To ensure that this system works properly, it is necessary to maintain the same rotation speed for all four wheels. The ABS sensor measures the speed of rotation and transmits it to the Vehicle’s Engine Control Module. This data is used by ABS to prevent sudden braking from locking the brakes. The ABS computer will detect if one wheel turns slower than the other when the brakes are applied. This can cause the vehicle to become unstable and skid. The ABS system is activated to assist the driver in controlling steering and brake by interfering with the locked wheels. ABS sensor is also known as “Wheel Speed Sensor” And “ABS Brake Sensor.” . Modern vehicles are equipped with ABS sensors which interact with sensors such VSC, ESP and ASR to provide vehicle safety.
Depending on which type of brake system you have, your vehicle may have one to four ABS sensors.
How does the ABS Sensor work?
ABS sensors can be classified into passive or active types.
ABS Sensors of Passive Type
Passive sensors require a toothed wheel. It is smaller and more sensitive than active sensors. It starts to work when the wheel reaches a specified speed. Because of their simplicity, they are much easier to control and far more durable than other wheels. They cannot also work in reverse. They cannot therefore determine the direction of movement.
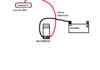
Passive sensors typically consist of a toothed wheels, a coil copper wire wound around a magnetic core, as well as a permanent magnet. The wheel hub houses the gear wheel. It rotates with the wheel and alters the magnetic field. The magnet is connected to the pole pin in the coil. The coil can measure the alternating voltage signal created by this magnetic field. The wheel’s rotational speed determines whether the voltage signal changes or rises. The signal is converted into a digital signal, and sent to ABS Control Module. This allows for calculations like vehicle speed, rotational speed, and kilometer information to be done.
ABS Sensors of Active Type
For active type sensors to function, an external energy source must be available. It can be divided into two groups.
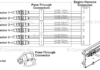
Hall-Type Sensors: Transmit the voltage difference to control unit as a signal wave by responding to magnetic field changes. They do not have to rotate in order to function with non-contact magnetic field detection. They can work at extremely low speeds and are reliable.
Magneto Resistive (AMR), Sensors This is the most expensive ABS sensor, but it is also the most advanced. These sensors can detect the direction of rotation and transmit signals more reliably than other types. It can measure the magnetic field cross-direction with the ABS sensor attached to the magnetic encoder. This means that speed and rotation direction can both be determined more efficiently.
Active sensors are more sensitive. They detect speeds below 0.06 mph. They are vital for TCS (Traction Control System-Antiskid System), which prevents the wheels from losing traction. Pulse Width Modulation is used to generate an active sensor that transmits it to ECM.
Is the ABS Sensor Mounted Where?
The ABS sensor is usually located in each wheel’s hub/rotor. Some rear-wheel drive vehicles have it mounted on the differential.
ABS Sensor Malfunction Symptoms
The ABS sensor can be damaged by road debris, brake pad dust and dirt. It is essential to check and clean the sensors at regular intervals as specified in the manuals for optimal performance.
The ABS light on your instrument cluster is one of the most important indicators that you have an ABS sensor problem. A significant loss in traction can also occur when driving on slippery roads. The ABS sensor may not always be to blame in this instance. The ECM could be unable to receive the required signals from cables or sockets. Before replacing the sensor, make sure to inspect the components involved and replace any that are defective.
- – One of the ABS or brake warning lights, located on the instrument panel.
- – Increased vehicle’s braking distance
- If the ABS sensor sends a wrong signal, the ECM might think that the vehicle may be skidding. In this case, pumping could occur when the brake is applied.
- – Vehicle sliding or skidding on slippery and wet roads
- – When the brake is applied, the vehicle pulls to one end.
- – Fault code stored on the OBD system
- Cruise Control is disabled