What is the P012D fault number? What is the description of the Turbocharger/Supercharger Input pressure Sensor Circuit High malfunction How do you fix the P012D fault code What are the symptoms and causes for the P012D fault codes?
What is the P012D Fault code? What does it stand for?
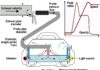
One of the most common symptoms associated with a Turbocharger/Supercharger inlet pressure (TCIP) sensor circuit malfunction is poor engine performance. Other engine components can also cause these symptoms. When the powertrain control module, PCM detects that voltage from turbo inlet pressure sensor has reached too high, a P012D fault is recorded.
Supercharging and turbocharging increase the pressure in the intake manifold. This increases engine power by drawing more air into the combustion chamber. These systems include an inlet for air filtering. The inlet pressure sensor of the PCM is used to monitor and regulate inlet air pressure. When the voltage signal exceeds the manufacturer’s programed limits, the code P012D will be triggered.
The P012D fault code can affect vehicles of all makes and models, including Ford, Dodge, Saturn, Nissan (especially the F-150), Subaru, Honda, Honda, Honda, Honda, Honda, Honda, Subaru, Honda, Honda, Honda, Honda, Dodge, Saturn, Nissan, Subaru and Honda.
This fault code is closely linked to P012A/P012B/P012C/P012E.
What causes the P012D fault code?
Here are some reasons why P012D should be set.
- – Defective Supercharger / Turbocharger inlet Pressure Sensor
- Harnesses that are damaged, frayed or broken
- – Connector problems such as loose, overheated, or corroded
- – Electrical system problems
- – Damaged or clogged air filter
- – Defective PCM
What are the symptoms of the P012D fault code?
These symptoms may be present if you own a vehicle that has the P012D code:
- – Illumination at the check engine lights
- – Low engine performance
- – Engine Stalling and Stalling
- – Increased fuel use
- – Engine making unusual noises
- – The vehicle may switch to failsafe mode
How to Fix the P012D Fault Code
Before replacing any components, inspect the system carefully. This type of failure is most often caused by physical damage. The harness must be inspected carefully as it is likely to be located in extremely hot areas.
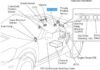
Refer to the “Throttle Output” section to determine which sensor’s circuit has gone haywire. You will find it on the side just after the throttle valve, or near the intake manifold. The throttle valve is normally mounted above or near the intake manifold. Locate the sensor and trace the wires leading to it. Repair any frayed / frayed or cut wires that might cause problems.
Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, the location of the sensor might vary. You can remove the connector if you have access to it. Then, check for corrosion. A sign of corrosion is the green color. Visually inspect all grounded wires. Replace worn or damaged connectors.
The circuit fuse should be checked. The fuse box is located usually under the instrument panel or behind the glovebox. Check the fuse box and locate it. If the fuse is broken, replace it.
Make sure to check the air filter. A blocked filter can lead to low pressure. It is important to replace the filter if it becomes clogged or has any damage, such as oil or water.
The circuit should undergo basic electrical testing. (i.e. Verify continuity and check for shorts to ground or power. If there is an open circuit or short circuit, it indicates that something needs to be fixed.
If everything seems to be in order, the turbo/supercharger intake pressure sensor should first be checked and then replaced if needed.